UAE Corporate Tax - Public Consultation Document
UAE Corporate Tax - Public Consultation Document
Download Aurifer’s reply to the Public Consultation initiated by the UAE Ministry of Finance in regard to the implementation of Corporate Income Tax in the UAE as of June 2023.
Scoring Tax Exemptions in Qatar
Scoring Tax Exemptions in Qatar
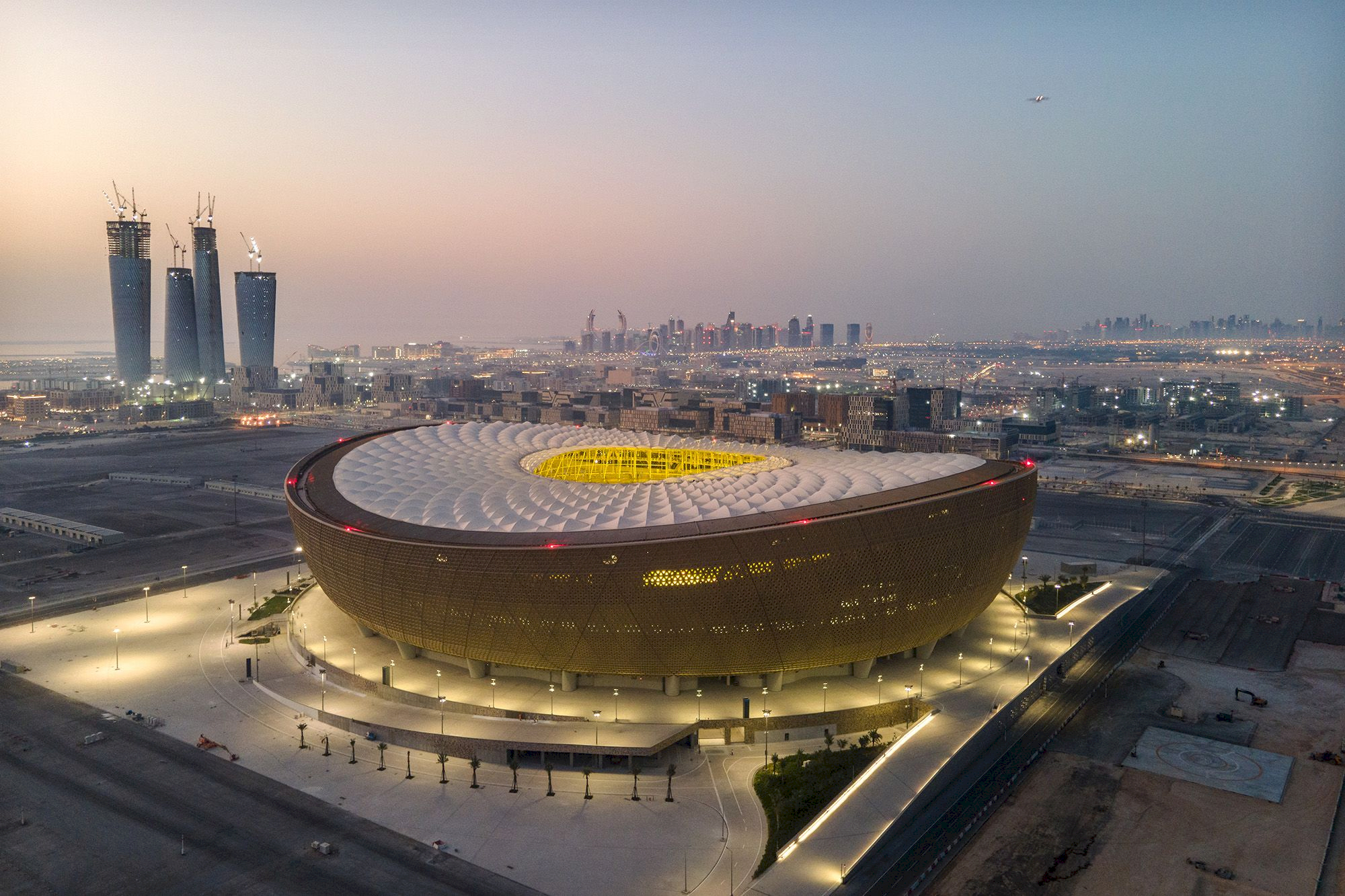
International sports bodies typically insist on obtaining widespread tax exemptions as a precondition to awarding the hosting rights to a bidder. This also applies for events organized by the Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA). FIFA’s biggest event, the Football World Cup, will kick off later this month in Qatar.
Obtaining tax exemptions is such a sensitive topic for sports organizations that there have even been instances where the events have entirely moved to another country because a country was unable to grant the exemption. For example, the T20 Cricket World Cup was moved from India to the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Oman last year because the Indian Government did not offer the exemptions in time.
In Qatar, even though Qatar has Free Zones, only the Qatar Financial Centre (QFC) issues its own tax framework. It applies next to the general tax framework applicable in the rest of the State of Qatar. We will be looking at these frameworks in this article.
Claiming Tax Exemptions (Substantive Aspects)
For mainland Qatar, Ministerial Decision No. 9 of 2022 (Ministerial Decision) issued earlier this year on 25 August 2022 = provides details on the exemptions available to different parties, based on Government Guarantee No. (3) dated 22 February 2010 (Government Guarantee) issued by the State of Qatar to FIFA.
The most comprehensive exemption benefits are provided to FIFA itself and its affiliates (whether residents or non-residents). They are totally exempt from any taxes.
Contractors are granted a limited exemption to the extent of all taxes on import, export or transfer of goods, services and rights related to the activities of the World Cup, if the goods are imported for their use by:
- The Contractors themselves in Qatar,
- The Contractors, with the possibility of re-exporting the goods,
- The Contractors, with the possibility to donate to sports entities, charitable foundations etc.
Individuals employed or appointed by the following, are also exempt from individual taxes on payments, fringe benefits or amounts paid or received in relation to the World Cup, until 31 December 2023:
- FIFA,
- FIFA’s affiliates,
- Continental or National Football Associations,
- Event broadcasters,
- Suppliers of goods,
- Works contractors and
- Service providers.
This exemption also covers Personal Income Taxes for those individuals who enter and exit Qatar between 60 days before the first match (21 September 2022) until 60 days after the final match (16 February 2023), as long as they do not permanently reside in Qatar. This exemption may be void of much effect, given the absence of Personal Income Tax in Qatar.
An Exemption from Excise tax is to be obtained by way of refund, by providing documents like purchase invoices and bank details.
Claiming The Exemptions - Logistical Aspects
For exemptions granted by the General Tax Authority (GTA), there is no requirement to register with the GTA. Instead, FIFA (through the Supreme Committee for Delivery and Legacy (Supreme Committee)) prepared a list of exempted entities and individual, containing data such as the nature of contracted works, term and value of the contract, and the residency of the contracting party.
The Supreme Committee then provides the GTA the relevant documentation (Articles of Associations of companies, addresses of individuals etc.) in regard to the organisation or individuals for whom the Tax Exemption is applied.
For claiming customs duty exemptions with the General Authority of Customs (GAC), (and unlike the procedure with the GTA), the claimants need to register with the GAC.
Here too, FIFA approves the list for the Supreme Committee to provide to the GAC to entitle those entities to exemptions from customs duties and fees. Based on this list, the GAC provides the listed entities amongst others with facilities in regard to electronic customs clearance.
In this regard, the GAC also earlier this year launched a ‘Sports Events Management System’ to facilitate customs procedures during sporting events, including the World Cup. This system provides electronic services for the clearance of goods, including easy registrations, accelerated customs procedures, and the inclusion of a special unit to facilitate approvals for incoming shipments.
There may be some interesting questions on the applicability of the Ministerial Decision, including:
- To what extent are the activities ‘directly or indirectly’ related to the activities of the World Cup? For example, does it include online betting platforms involved in placing bets on the matches? Would it include businesses that are involved in ancillary aspects to the World Cup such as general tourism consequent to the World Cup?
- Would match fee or advertisement / sponsorship / award income earned by the footballers in relation to the World Cup also be covered under the Ministerial Decision?
- Where an event broadcaster obtains substantial advertisement income from brand sponsors during the broadcast of the match or match related activities, is such income also exempt from taxes?
QFC - Tax Exemption Regime for the World Cup
The QFC in its Concessionary Statement of Practice (Statement) explicitly provides that a QFC entity which is a:
- FIFA subsidiary – is exempt from Corporation tax and any other charge, levy, penalty or interest related thereto;
- FIFA Host Broadcaster or a Local Organizing Committee (LoC) Entity – is exempt from Tax ‘in relation to taxable profits that are derived from activities carried on for the purposes of the World Cup’.
The major conditions for such QFC entities to claim the exemption are as follows:
- Such QFC entities have genuine economic substance in Qatar,
- The QFC entity operates in terms of the license and upon authorization of the Qatar Financial Centre Regulatory Authority (QFCRA),
- An Advanced Ruling has been applied for by the QFC entity and granted by the QFC, confirming the exempt status of such QFC entity,
- The QFC entity is included in the list provided by FIFA to the QFC Tax Department,
- The sole or main purpose of such QFC entity is not avoidance of tax,
- The QFC Tax Department is satisfied that granting the exemption is not in breach of international tax principles set out in the BEPS Project minimum standards.
The potential activities that can be developed in the QFC are limited, and therefore not all types of businesses can set up in the QFC.
No VAT – No VAT Exemption
Even though Qatar is a part of the GCC VAT Agreement and committed to implement VAT in the same vein as its neighboring countries of the UAE, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), Bahrain and Oman have done, it has not yet enacted any legislation.
Therefore, there is currently no need for a VAT exemption for the World Cup. Who knows, VAT may be introduced shortly after the organization of the World Cup?
Exemptions Worth the Trouble?
Granting tax exemptions for international sporting events are sometimes controversial. The public in some hosting countries do not always believe they receive a return on investments from the event. While Qatar has spent substantial amounts of money on the construction of infrastructure, the effect of the tax exemptions is rather limited, and at least for Qatar, it seems to have been worth the investment. In any case, the exemptions are a precondition, without which a country cannot bid. After the UAE had hosted the FIFA Club World Cup a number of times, Saudi Arabia will now be looking at hosting the Asian Winter Games in 2029. Those countries have given similar tax concessions to the international organizations managing the events.
For future possible events in the UAE, it will also be interesting to see how the sporting organizations and the tax authorities will deal with the Corporate Income Tax (CIT) which is to be introduced in the UAE in June 2023. The relationship may be anything between an unbridled and full-fledged exemption (if the UAE is willing to do so), or it may lead to rather interesting tax claims (like the Formula 1 case on Permanent Establishment (PE) in India a few years ago, which was decided by the courts in the tax authority’s favor). Time alone can tell.
Almost 5 years down the line for VAT in the GCC – what’s next?
Almost 5 years down the line for VAT in the GCC – what’s next?
Almost 5 years down the line for VAT in the GCC – what’s next?
As we approach 31 December 2022, the UAE and KSA will be celebrating 5 years of applying VAT. A rollercoaster ride for many in the region, authorities, advisers and in house tax managers.
We wrote in 2017 about the challenges of drafting VAT legislation in the GCC before its implementation (https://aurifer.tax/news/the-challenges-of-drafting-tax-legislation-and-implementing-a-vat-in-the-gcc/?lid=482&p=21).
We pondered whether the GCC was potentially going to be far ahead of other jurisdictions because of the Electronic Services System (“ESS”) the GCC VAT Agreement was going to implement, foreseen in article 71 of the Agreement (https://aurifer.tax/news/future-of-vat-in-the-eu/?lid=482&p=22). The GCC however never implemented the ESS. It is therefore missing an important instrument to integrate all GCC members under a single comprehensive regional VAT framework.
After almost 5 years, it’s worth taking a step back and looking at what occurred.
6 countries to implement, only 4 did
The GCC consists of six countries, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Bahrain, Oman, Kuwait and Qatar. All countries were supposed to introduce VAT in a short span of time. The UAE and KSA did so on 1 January 2018, Bahrain on 1 January 2019, and Oman on 16 April 2021. For Qatar, rumours ebb and flow on an implementation of VAT after the World Cup, but officials are tight lipped. In terms of Kuwait, a new government is not likely to put this on the table – at least, in the near future.
The intention to implement almost simultaneously was taken with the idea of avoiding arbitrage – considering the geographical proximity between the states - and potential issues with fraud.
5% was supposed to be the rate
All 4 countries kicked off with 5% VAT, as it is foreseen in the GCC VAT Agreement as well (article 25). Saudi Arabia was the first one to hike the rate to 15% on 1 July 2020. Bahrain increased to 10% on 1 January 2022.
The increases were implemented for the same reason, as the tax was implemented for in the first place, i.e. fiscal stability. The implementation came off the back of a protracted period of running deficits for many Gulf countries. There is currently a bounce back, but how long it will take is unclear, and therefore hard to predict whether it will impact fiscal policy in the short run.
Saudi Arabia, by way of its Finance Minister, had already stated in 2021 that it would consider revising the VAT rate downwards after the pandemic. If it will happen, it will happen soon.
It’s safe to say the other GCC countries could still revise the rate upwards or downwards, depending on their specific fiscal situation.
Interestingly, the increase of the VAT rate to 15% also spawned a new tax in KSA, the Real Estate Transfer Tax (“RETT”). This new tax in KSA aimed to solve the issue of unregistered sellers, and reduce the taxes on real estate sales. Since its introduction, the RETT legislation has been amended multiple times.
The GCC countries were supposed to have numerical VAT numbers, Oman didn’t follow
In the framework of the GCC, the idea was floated to have numbers as VAT numbers. Hence, the UAE has a 1 before the number, Bahrain a 2 and Saudi a 3. Oman however choose letters and put “OM” before the number.
In the EU, VAT numbers are also composed of letters and numbers. Two letters make up the first two symbols of the VAT number and refer to a country, e.g. “LU” refers to Luxembourg (see https://taxation-customs.ec.europa.eu/vat-identification-numbers_en).
Zero rates for services are perceived a complication
5 years in, the application to zero-rate VAT on exported services, i.e., services provided to recipients outside of the GCC, remains complicated for businesses to apply and inconsistent between the GCC member states.
Although the GCC VAT Agreement for place of supply purposes looks like the EU VAT directive, from the outset, each GCC member state chose different approaches towards the place of supply of services.
B2B services were not simply located in the country of the recipient, as they are in the EU since 2010, and as is recommended by the OECD in its VAT/GST Guidelines on B2B services.
Based on an interpretation of article 34(1)(c) of the GCC VAT Agreement as laying down the rule, and including a benefit test, GCC countries have embarked on a conservative and selective interpretation of the zero rate on supplies made from a GCC country to abroad.
That conservative interpretation is not necessarily mirrored when those services are received, as there is no benefit test required there.
The rule is therefore applied unequal, and as shown by both the UAE and KSA, they felt the rule required amendments to the provision itself (https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/uae-considerably-restricts-application-vat-zero-rate-services-vanhee/). Those amendments, and ensuing clarifications have not necessarily led to more clarity.
Unfortunately, Bahrain and Oman went down the same road. A too conservative view of zero rates, can put a strain on foreign investments, as it is not easy to obtain refunds for foreign businesses (as amongst others the Saudi example shows).
As a matter of fact, disputes are common among businesses in the GCC over the VAT treatment of cross-border services due to the difference in the domestic legislation between the GCC member states and in the absence of the ESS.
Divergent policy options
The GCC VAT Framework Agreement allowed for broad policy options in the education sector, health sector, real estate sector and local transport sector. In addition, for the oil & gas sector zero rates were allowed to be implemented as well, and the financial sector could benefit from a deviating regime as well. Depending on the individual requirements and policies, the GCC Member States have implemented substantially different regimes.
None of the GCC countries so far have amended those policies in the aforementioned sectors. The UAE did move from a system where the B2B sales of diamonds was taxed, to a system where it is subject to a reverse charge as from 1 June 2018.
Tax Authority approaches
So far, in the region ZATCA has shown the most grit in terms of audits, and has lengths ahead of the other countries in terms of tax audits and disputes. KSA also had the best equipped tax authority in 2018 when VAT was introduced, although it did have to go through an organizational revamp. The UAE comes second, which is remarkable for a tax authority which only kicked off in 2017. It has been very much a rules and process based organization, which has a lot of positive effects, such as tax payers feeling treated in the same way. UAE auditors now often also give the opportunity to tax payers to voluntarily disclose their liabilities before closing the audit, which is a novely approach in the region.
The Bahraini and Omani tax authority, have been taking a more relaxed approach towards audits and disputes.
Having said the above, it's all not all 'sticks' with the tax authorities. We have also observed in this 5 years, how the tax authorities, especially in KSA and the UAE, played a their role to alleviate tax from being a burden to businesses and encouraging tax compliance - a fairly new culture of this scale. The amnesty programmes, first introduced by the KSA in 2020 and again, recently paved the way on encouraging tax compliance for businesses. The UAE also introduced their amnesty programme this year with the same intention. Perhaps, this could be a temporary solution to gear the economy back on track post pandemic. On whether it will be the norm, is yet to be seen in the next coming years.
What the future will bring
An old-fashioned system was put in place, yet one that has proven its use in revenue collection. It also worked, given the substantial revenues gained from VAT.
The GCC did not opted to immediately adopt more modern, electronic systems as these exist elsewhere (e.g. since a long time in Brazil, but also China).
However, it was identified that E-invoicing was the way to go in the medium run. This is again trodding down a proven path. As often in the GCC, the UAE and KSA show the way. KSA has made E-invoicing mandatory. The UAE and Bahrain have already suggested they will do the same very soon.
No GCC countries have yet announced they will adopt real-time reporting. KSA may be the closest to a potential adoption, given that once phase 2 enters into force in 2023, ZATCA, the KSA tax authority will have access to substantial transactional data. It will allow it to pre-fill the VAT return, and potentially even in real time calculate the VAT.
We'll see what the future will bring, and for sure in another five years matters will have evolved again drastically, given the pace of changes in the region.
Safe to say that the next 5 years will be equally exciting.
How anti-avoidance provisions can curtail the application of Double Tax Treaties, including in the UAE?
The Ministry of Finance (MoF) of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) recently announced that the draft Corporate Tax (CT) law is going to be released soon, and likely within the month of September. This is impactful news for businesses in the UAE. Many businesses are already in the process of taking steps to plan their affairs in such a way that their operations are tax compliant and tax optimized at the same time.
The UAE’s international position will change after the implementation of corporate tax. Some jurisdictions may no longer view the UAE as a tax haven (although the Free Zone businesses may still benefit from a 0% rate). Other tax authorities may therefore change their perspective on the UAE and be more inclined to grant the benefits under the double tax treaties.
Businesses on the other hand, will no longer view the UAE as a conduit jurisdiction with an extensive treaty network, through which they can avail tax treaty benefits. While the 9% headline rate is still comparatively low, the implementation of CT may also discourage taxpayers seeking out the UAE solely for tax purposes.
A recurring point of dispute between the tax authority and businesses in almost every country having a CT regime has been drawing the line between tax planning, tax avoidance and tax evasion. Once the UAE CT regime settles, the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) of the UAE may indeed pay more attention towards countering tax avoidance and tax evasion arrangements or transactions.
In this article, we will revisit the evergreen discussion of tax planning, tax avoidance and tax evasion, with an emphasis on the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). To begin, let us examine the meaning of the terms tax avoidance and tax evasion and the differences between the two terms.
Tax avoidance has traditionally been considered as lawful. It can be described as planning for the purposes of minimizing the tax burden within the legal framework. Tax evasion on the other hand is considered unlawful, and often requires an intentional and a potential fraudulent element.
In the GCC, tax authorities resort rather quickly to suggesting a taxpayer has committed tax evasion, even when the situation concerns simple non-compliance.
While not considered unlawful, tax avoidance has been considered harmful. This is why countries around the world, including the GCC Member States, are implementing domestic rules to counter aggressive or harmful tax planning in line with international standards.
The OECD tried to address this point by way of the ‘Main Purpose Test’ (MPT). The MPT was included in the OECD’s Model Tax Convention in its 2003 version. We are paraphrasing, but the principle stated that benefits under a double tax treaty should not be granted where the main purpose of setting up a structure was for tax purposes as the tax benefits resulting from that structure would go counter the object and purpose of those treaties.
Another common mechanism proposed in tax treaties to avoid the improper use of tax treaties, is the ‘Beneficial Ownership’ (BO) requirement. It mainly applies to passive income (e.g., dividends, interests, and royalties). The BO concept provides that where an item of income is paid to a resident of a Contracting State acting in the capacity of an agent or a nominee, it would be inconsistent with the object and purpose of the source state to grant an exemption or relief, merely because the direct recipient is a resident of the other Contracting State. In such a case, the direct recipient, on account of being merely an agent, nominee, conduit, fiduciary, or administrator, would not be able to obtain the benefits of the treaty. This is especially evident if such recipient is legally or contractually bound to pass on the payment received to another person. BO disputes often end up before the courts, because the burden of proof for the taxpayer is not easily met.
The 2008 Financial Crisis put the discussion on tax avoidance and aggressive tax planning firmly on governments’ agenda. Following the Financial Crisis, public opinion shifted towards ensuring that big corporations pay their fair share of taxes and pressured countries to implement rules to discourage such behaviors.
As a result, the OECD established what is known as the ‘Inclusive Framework’ (IF), which was open to both OECD and non-OECD members (currently at 141 members) to engage in discussions and create rules for countering Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS). It is formally known as the OECD/G20 BEPS Project (BEPS Project 1.0) which identified 15 Action Points in 2015.
Out of the 15 Action Points, one of the most important action plans was BEPS Action 6 - Prevention of Tax Treaty Abuse, which also formed one of the four minimum standards. BEPS Action 6 addresses treaty shopping activities that would be viewed as avoidance.
BEPS Action 6 requires IF members, amongst others, to include an express statement in their treaties that their common intention is to eliminate double taxation without creating opportunities for non-taxation or reduced taxation through tax evasion or avoidance, including through treaty shopping arrangements.
Anti-avoidance rules aim amongst others to avoid conduit arrangements. For example, State A has a domestic withholding tax rate for dividends of 25%. State A and State B have negotiated a tax treaty where the source withholding tax rate for dividends is reduced to 5%. A resident in State B receives dividends from State A and claims the reduced treaty rate of 5% source withholding.
However, the resident in State B has an obligation to redistribute the dividend income to a resident in State C. State A and State C do not have a tax treaty in place. It can be observed that there is no BO in State B due to its obligation to pass the payment onto another party. Clearly, such payment is not made for the benefit of any resident in State B nor for enhancing economic cooperation between States A and B. Instead, the benefit would be received by the resident of a third State (i.e., State C). This clearly shows that the treaty has been misused or abused by the resident of State B, against the intention, object, and purpose of the treaty between States A and B.
To combat misuse of the treaty like the case described above, BEPS Action 6 seeks IF members to implement a ‘minimum standard’ in all its treaties. The minimum standard can be either of the following:
- The combined approach of a Limitation of Benefits (LOB) and a Principal Purpose Test (PPT) rule,
- The PPT rule alone, or
- The LOB rule supplemented by a mechanism that would deal with conduit financing arrangements not already dealt with in tax treaties.
As a consequence, many IF members’ tax treaties have been updated to include, at least, a PPT rule. This is done by way of signing and ratifying the Multilateral Instrument (MLI) as it allows IF members to update multiple bilateral tax treaties simultaneously. The PPT rule looks a lot like the MPT. True to its name, if one of the principal purposes of an arrangement is to obtain a benefit, the PPT rule may be triggered. This clear intention has also been expressed in the wordings of the preamble incorporated in the OECD Model Tax Convention 2017.
Due to the lack of case law, the impact of the PPT rule is rather uncertain for now and the interpretation of the PPT rule may vary across jurisdictions. It may be possible that the cases that were successfully tested before the courts of law earlier may not survive the PPT rule if they were to be presented before the courts today, provided that the PPT rule was applicable at the time of the transaction or arrangement.
What is certain is that taxpayers ought to be very careful in tax planning so that the structures do not fall foul of the PPT rule. When deciding on the country to make an investment in or the structure of a transaction or arrangement, taxpayers ought to clearly record the non-tax reasons (main/principal purposes) for selecting a certain jurisdiction over another. Evidence can be maintained through internal emails, memos, and minutes outlining the reasons for selecting a country. For example:
- A country is preferred due to a favourable corporate law regime.
- A country is preferred due to the presence of multilingual or highly qualified employees.
- A country is preferred as it is politically and socially stable.
- A country is preferred as it has a strong banking infrastructure where it is easy to obtain credit.
Despite the above safeguards, if the tax authority does reasonably conclude that one of the principal purposes of invoking the treaty was to obtain a tax benefit, the taxpayer ought to ensure that it can establish (i.e., prove) that the benefit obtained was indeed within the object and purpose of the tax treaty.
Finally, as mentioned before, public opinion against tax avoidance is stronger than ever. The relevance of the PPT to future transactions cannot be overstated. Arrangements that may have been successfully litigated before the courts of law until a few years ago, may not be as successful from now on. Therefore, taxpayers may find advance rulings to be attractive as it is important to avoid future issues.
It will be interesting to see how the UAE and the other GCC countries will approach such abusive arrangements and its possible disputes. In the meantime, it is apparent that either through the MLI or through bilateral double tax treaties, the PPT continues to be important. It is vital to consider such anti-avoidance provisions now in order to create future proof structures.
UAE Corporate Tax - Public Consultation Document
UAE Corporate Tax - Public Consultation Document
Download Aurifer’s reply to the Public Consultation initiated by the UAE Ministry of Finance in regard to the implementation of Corporate Income Tax in the UAE as of June 2023.
Scoring Tax Exemptions in Qatar
Scoring Tax Exemptions in Qatar
International sports bodies typically insist on obtaining widespread tax exemptions as a precondition to awarding the hosting rights to a bidder. This also applies for events organized by the Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA). FIFA’s biggest event, the Football World Cup, will kick off later this month in Qatar.
Obtaining tax exemptions is such a sensitive topic for sports organizations that there have even been instances where the events have entirely moved to another country because a country was unable to grant the exemption. For example, the T20 Cricket World Cup was moved from India to the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Oman last year because the Indian Government did not offer the exemptions in time.
In Qatar, even though Qatar has Free Zones, only the Qatar Financial Centre (QFC) issues its own tax framework. It applies next to the general tax framework applicable in the rest of the State of Qatar. We will be looking at these frameworks in this article.
Claiming Tax Exemptions (Substantive Aspects)
For mainland Qatar, Ministerial Decision No. 9 of 2022 (Ministerial Decision) issued earlier this year on 25 August 2022 = provides details on the exemptions available to different parties, based on Government Guarantee No. (3) dated 22 February 2010 (Government Guarantee) issued by the State of Qatar to FIFA.
The most comprehensive exemption benefits are provided to FIFA itself and its affiliates (whether residents or non-residents). They are totally exempt from any taxes.
Contractors are granted a limited exemption to the extent of all taxes on import, export or transfer of goods, services and rights related to the activities of the World Cup, if the goods are imported for their use by:
- The Contractors themselves in Qatar,
- The Contractors, with the possibility of re-exporting the goods,
- The Contractors, with the possibility to donate to sports entities, charitable foundations etc.
Individuals employed or appointed by the following, are also exempt from individual taxes on payments, fringe benefits or amounts paid or received in relation to the World Cup, until 31 December 2023:
- FIFA,
- FIFA’s affiliates,
- Continental or National Football Associations,
- Event broadcasters,
- Suppliers of goods,
- Works contractors and
- Service providers.
This exemption also covers Personal Income Taxes for those individuals who enter and exit Qatar between 60 days before the first match (21 September 2022) until 60 days after the final match (16 February 2023), as long as they do not permanently reside in Qatar. This exemption may be void of much effect, given the absence of Personal Income Tax in Qatar.
An Exemption from Excise tax is to be obtained by way of refund, by providing documents like purchase invoices and bank details.
Claiming The Exemptions - Logistical Aspects
For exemptions granted by the General Tax Authority (GTA), there is no requirement to register with the GTA. Instead, FIFA (through the Supreme Committee for Delivery and Legacy (Supreme Committee)) prepared a list of exempted entities and individual, containing data such as the nature of contracted works, term and value of the contract, and the residency of the contracting party.
The Supreme Committee then provides the GTA the relevant documentation (Articles of Associations of companies, addresses of individuals etc.) in regard to the organisation or individuals for whom the Tax Exemption is applied.
For claiming customs duty exemptions with the General Authority of Customs (GAC), (and unlike the procedure with the GTA), the claimants need to register with the GAC.
Here too, FIFA approves the list for the Supreme Committee to provide to the GAC to entitle those entities to exemptions from customs duties and fees. Based on this list, the GAC provides the listed entities amongst others with facilities in regard to electronic customs clearance.
In this regard, the GAC also earlier this year launched a ‘Sports Events Management System’ to facilitate customs procedures during sporting events, including the World Cup. This system provides electronic services for the clearance of goods, including easy registrations, accelerated customs procedures, and the inclusion of a special unit to facilitate approvals for incoming shipments.
There may be some interesting questions on the applicability of the Ministerial Decision, including:
- To what extent are the activities ‘directly or indirectly’ related to the activities of the World Cup? For example, does it include online betting platforms involved in placing bets on the matches? Would it include businesses that are involved in ancillary aspects to the World Cup such as general tourism consequent to the World Cup?
- Would match fee or advertisement / sponsorship / award income earned by the footballers in relation to the World Cup also be covered under the Ministerial Decision?
- Where an event broadcaster obtains substantial advertisement income from brand sponsors during the broadcast of the match or match related activities, is such income also exempt from taxes?
QFC - Tax Exemption Regime for the World Cup
The QFC in its Concessionary Statement of Practice (Statement) explicitly provides that a QFC entity which is a:
- FIFA subsidiary – is exempt from Corporation tax and any other charge, levy, penalty or interest related thereto;
- FIFA Host Broadcaster or a Local Organizing Committee (LoC) Entity – is exempt from Tax ‘in relation to taxable profits that are derived from activities carried on for the purposes of the World Cup’.
The major conditions for such QFC entities to claim the exemption are as follows:
- Such QFC entities have genuine economic substance in Qatar,
- The QFC entity operates in terms of the license and upon authorization of the Qatar Financial Centre Regulatory Authority (QFCRA),
- An Advanced Ruling has been applied for by the QFC entity and granted by the QFC, confirming the exempt status of such QFC entity,
- The QFC entity is included in the list provided by FIFA to the QFC Tax Department,
- The sole or main purpose of such QFC entity is not avoidance of tax,
- The QFC Tax Department is satisfied that granting the exemption is not in breach of international tax principles set out in the BEPS Project minimum standards.
The potential activities that can be developed in the QFC are limited, and therefore not all types of businesses can set up in the QFC.
No VAT – No VAT Exemption
Even though Qatar is a part of the GCC VAT Agreement and committed to implement VAT in the same vein as its neighboring countries of the UAE, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), Bahrain and Oman have done, it has not yet enacted any legislation.
Therefore, there is currently no need for a VAT exemption for the World Cup. Who knows, VAT may be introduced shortly after the organization of the World Cup?
Exemptions Worth the Trouble?
Granting tax exemptions for international sporting events are sometimes controversial. The public in some hosting countries do not always believe they receive a return on investments from the event. While Qatar has spent substantial amounts of money on the construction of infrastructure, the effect of the tax exemptions is rather limited, and at least for Qatar, it seems to have been worth the investment. In any case, the exemptions are a precondition, without which a country cannot bid. After the UAE had hosted the FIFA Club World Cup a number of times, Saudi Arabia will now be looking at hosting the Asian Winter Games in 2029. Those countries have given similar tax concessions to the international organizations managing the events.
For future possible events in the UAE, it will also be interesting to see how the sporting organizations and the tax authorities will deal with the Corporate Income Tax (CIT) which is to be introduced in the UAE in June 2023. The relationship may be anything between an unbridled and full-fledged exemption (if the UAE is willing to do so), or it may lead to rather interesting tax claims (like the Formula 1 case on Permanent Establishment (PE) in India a few years ago, which was decided by the courts in the tax authority’s favor). Time alone can tell.
Almost 5 years down the line for VAT in the GCC – what’s next?
Almost 5 years down the line for VAT in the GCC – what’s next?
Almost 5 years down the line for VAT in the GCC – what’s next?
As we approach 31 December 2022, the UAE and KSA will be celebrating 5 years of applying VAT. A rollercoaster ride for many in the region, authorities, advisers and in house tax managers.
We wrote in 2017 about the challenges of drafting VAT legislation in the GCC before its implementation (https://aurifer.tax/news/the-challenges-of-drafting-tax-legislation-and-implementing-a-vat-in-the-gcc/?lid=482&p=21).
We pondered whether the GCC was potentially going to be far ahead of other jurisdictions because of the Electronic Services System (“ESS”) the GCC VAT Agreement was going to implement, foreseen in article 71 of the Agreement (https://aurifer.tax/news/future-of-vat-in-the-eu/?lid=482&p=22). The GCC however never implemented the ESS. It is therefore missing an important instrument to integrate all GCC members under a single comprehensive regional VAT framework.
After almost 5 years, it’s worth taking a step back and looking at what occurred.
6 countries to implement, only 4 did
The GCC consists of six countries, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Bahrain, Oman, Kuwait and Qatar. All countries were supposed to introduce VAT in a short span of time. The UAE and KSA did so on 1 January 2018, Bahrain on 1 January 2019, and Oman on 16 April 2021. For Qatar, rumours ebb and flow on an implementation of VAT after the World Cup, but officials are tight lipped. In terms of Kuwait, a new government is not likely to put this on the table – at least, in the near future.
The intention to implement almost simultaneously was taken with the idea of avoiding arbitrage – considering the geographical proximity between the states - and potential issues with fraud.
5% was supposed to be the rate
All 4 countries kicked off with 5% VAT, as it is foreseen in the GCC VAT Agreement as well (article 25). Saudi Arabia was the first one to hike the rate to 15% on 1 July 2020. Bahrain increased to 10% on 1 January 2022.
The increases were implemented for the same reason, as the tax was implemented for in the first place, i.e. fiscal stability. The implementation came off the back of a protracted period of running deficits for many Gulf countries. There is currently a bounce back, but how long it will take is unclear, and therefore hard to predict whether it will impact fiscal policy in the short run.
Saudi Arabia, by way of its Finance Minister, had already stated in 2021 that it would consider revising the VAT rate downwards after the pandemic. If it will happen, it will happen soon.
It’s safe to say the other GCC countries could still revise the rate upwards or downwards, depending on their specific fiscal situation.
Interestingly, the increase of the VAT rate to 15% also spawned a new tax in KSA, the Real Estate Transfer Tax (“RETT”). This new tax in KSA aimed to solve the issue of unregistered sellers, and reduce the taxes on real estate sales. Since its introduction, the RETT legislation has been amended multiple times.
The GCC countries were supposed to have numerical VAT numbers, Oman didn’t follow
In the framework of the GCC, the idea was floated to have numbers as VAT numbers. Hence, the UAE has a 1 before the number, Bahrain a 2 and Saudi a 3. Oman however choose letters and put “OM” before the number.
In the EU, VAT numbers are also composed of letters and numbers. Two letters make up the first two symbols of the VAT number and refer to a country, e.g. “LU” refers to Luxembourg (see https://taxation-customs.ec.europa.eu/vat-identification-numbers_en).
Zero rates for services are perceived a complication
5 years in, the application to zero-rate VAT on exported services, i.e., services provided to recipients outside of the GCC, remains complicated for businesses to apply and inconsistent between the GCC member states.
Although the GCC VAT Agreement for place of supply purposes looks like the EU VAT directive, from the outset, each GCC member state chose different approaches towards the place of supply of services.
B2B services were not simply located in the country of the recipient, as they are in the EU since 2010, and as is recommended by the OECD in its VAT/GST Guidelines on B2B services.
Based on an interpretation of article 34(1)(c) of the GCC VAT Agreement as laying down the rule, and including a benefit test, GCC countries have embarked on a conservative and selective interpretation of the zero rate on supplies made from a GCC country to abroad.
That conservative interpretation is not necessarily mirrored when those services are received, as there is no benefit test required there.
The rule is therefore applied unequal, and as shown by both the UAE and KSA, they felt the rule required amendments to the provision itself (https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/uae-considerably-restricts-application-vat-zero-rate-services-vanhee/). Those amendments, and ensuing clarifications have not necessarily led to more clarity.
Unfortunately, Bahrain and Oman went down the same road. A too conservative view of zero rates, can put a strain on foreign investments, as it is not easy to obtain refunds for foreign businesses (as amongst others the Saudi example shows).
As a matter of fact, disputes are common among businesses in the GCC over the VAT treatment of cross-border services due to the difference in the domestic legislation between the GCC member states and in the absence of the ESS.
Divergent policy options
The GCC VAT Framework Agreement allowed for broad policy options in the education sector, health sector, real estate sector and local transport sector. In addition, for the oil & gas sector zero rates were allowed to be implemented as well, and the financial sector could benefit from a deviating regime as well. Depending on the individual requirements and policies, the GCC Member States have implemented substantially different regimes.
None of the GCC countries so far have amended those policies in the aforementioned sectors. The UAE did move from a system where the B2B sales of diamonds was taxed, to a system where it is subject to a reverse charge as from 1 June 2018.
Tax Authority approaches
So far, in the region ZATCA has shown the most grit in terms of audits, and has lengths ahead of the other countries in terms of tax audits and disputes. KSA also had the best equipped tax authority in 2018 when VAT was introduced, although it did have to go through an organizational revamp. The UAE comes second, which is remarkable for a tax authority which only kicked off in 2017. It has been very much a rules and process based organization, which has a lot of positive effects, such as tax payers feeling treated in the same way. UAE auditors now often also give the opportunity to tax payers to voluntarily disclose their liabilities before closing the audit, which is a novely approach in the region.
The Bahraini and Omani tax authority, have been taking a more relaxed approach towards audits and disputes.
Having said the above, it's all not all 'sticks' with the tax authorities. We have also observed in this 5 years, how the tax authorities, especially in KSA and the UAE, played a their role to alleviate tax from being a burden to businesses and encouraging tax compliance - a fairly new culture of this scale. The amnesty programmes, first introduced by the KSA in 2020 and again, recently paved the way on encouraging tax compliance for businesses. The UAE also introduced their amnesty programme this year with the same intention. Perhaps, this could be a temporary solution to gear the economy back on track post pandemic. On whether it will be the norm, is yet to be seen in the next coming years.
What the future will bring
An old-fashioned system was put in place, yet one that has proven its use in revenue collection. It also worked, given the substantial revenues gained from VAT.
The GCC did not opted to immediately adopt more modern, electronic systems as these exist elsewhere (e.g. since a long time in Brazil, but also China).
However, it was identified that E-invoicing was the way to go in the medium run. This is again trodding down a proven path. As often in the GCC, the UAE and KSA show the way. KSA has made E-invoicing mandatory. The UAE and Bahrain have already suggested they will do the same very soon.
No GCC countries have yet announced they will adopt real-time reporting. KSA may be the closest to a potential adoption, given that once phase 2 enters into force in 2023, ZATCA, the KSA tax authority will have access to substantial transactional data. It will allow it to pre-fill the VAT return, and potentially even in real time calculate the VAT.
We'll see what the future will bring, and for sure in another five years matters will have evolved again drastically, given the pace of changes in the region.
Safe to say that the next 5 years will be equally exciting.
How anti-avoidance provisions can curtail the application of Double Tax Treaties, including in the UAE?
The Ministry of Finance (MoF) of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) recently announced that the draft Corporate Tax (CT) law is going to be released soon, and likely within the month of September. This is impactful news for businesses in the UAE. Many businesses are already in the process of taking steps to plan their affairs in such a way that their operations are tax compliant and tax optimized at the same time.
The UAE’s international position will change after the implementation of corporate tax. Some jurisdictions may no longer view the UAE as a tax haven (although the Free Zone businesses may still benefit from a 0% rate). Other tax authorities may therefore change their perspective on the UAE and be more inclined to grant the benefits under the double tax treaties.
Businesses on the other hand, will no longer view the UAE as a conduit jurisdiction with an extensive treaty network, through which they can avail tax treaty benefits. While the 9% headline rate is still comparatively low, the implementation of CT may also discourage taxpayers seeking out the UAE solely for tax purposes.
A recurring point of dispute between the tax authority and businesses in almost every country having a CT regime has been drawing the line between tax planning, tax avoidance and tax evasion. Once the UAE CT regime settles, the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) of the UAE may indeed pay more attention towards countering tax avoidance and tax evasion arrangements or transactions.
In this article, we will revisit the evergreen discussion of tax planning, tax avoidance and tax evasion, with an emphasis on the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). To begin, let us examine the meaning of the terms tax avoidance and tax evasion and the differences between the two terms.
Tax avoidance has traditionally been considered as lawful. It can be described as planning for the purposes of minimizing the tax burden within the legal framework. Tax evasion on the other hand is considered unlawful, and often requires an intentional and a potential fraudulent element.
In the GCC, tax authorities resort rather quickly to suggesting a taxpayer has committed tax evasion, even when the situation concerns simple non-compliance.
While not considered unlawful, tax avoidance has been considered harmful. This is why countries around the world, including the GCC Member States, are implementing domestic rules to counter aggressive or harmful tax planning in line with international standards.
The OECD tried to address this point by way of the ‘Main Purpose Test’ (MPT). The MPT was included in the OECD’s Model Tax Convention in its 2003 version. We are paraphrasing, but the principle stated that benefits under a double tax treaty should not be granted where the main purpose of setting up a structure was for tax purposes as the tax benefits resulting from that structure would go counter the object and purpose of those treaties.
Another common mechanism proposed in tax treaties to avoid the improper use of tax treaties, is the ‘Beneficial Ownership’ (BO) requirement. It mainly applies to passive income (e.g., dividends, interests, and royalties). The BO concept provides that where an item of income is paid to a resident of a Contracting State acting in the capacity of an agent or a nominee, it would be inconsistent with the object and purpose of the source state to grant an exemption or relief, merely because the direct recipient is a resident of the other Contracting State. In such a case, the direct recipient, on account of being merely an agent, nominee, conduit, fiduciary, or administrator, would not be able to obtain the benefits of the treaty. This is especially evident if such recipient is legally or contractually bound to pass on the payment received to another person. BO disputes often end up before the courts, because the burden of proof for the taxpayer is not easily met.
The 2008 Financial Crisis put the discussion on tax avoidance and aggressive tax planning firmly on governments’ agenda. Following the Financial Crisis, public opinion shifted towards ensuring that big corporations pay their fair share of taxes and pressured countries to implement rules to discourage such behaviors.
As a result, the OECD established what is known as the ‘Inclusive Framework’ (IF), which was open to both OECD and non-OECD members (currently at 141 members) to engage in discussions and create rules for countering Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS). It is formally known as the OECD/G20 BEPS Project (BEPS Project 1.0) which identified 15 Action Points in 2015.
Out of the 15 Action Points, one of the most important action plans was BEPS Action 6 - Prevention of Tax Treaty Abuse, which also formed one of the four minimum standards. BEPS Action 6 addresses treaty shopping activities that would be viewed as avoidance.
BEPS Action 6 requires IF members, amongst others, to include an express statement in their treaties that their common intention is to eliminate double taxation without creating opportunities for non-taxation or reduced taxation through tax evasion or avoidance, including through treaty shopping arrangements.
Anti-avoidance rules aim amongst others to avoid conduit arrangements. For example, State A has a domestic withholding tax rate for dividends of 25%. State A and State B have negotiated a tax treaty where the source withholding tax rate for dividends is reduced to 5%. A resident in State B receives dividends from State A and claims the reduced treaty rate of 5% source withholding.
However, the resident in State B has an obligation to redistribute the dividend income to a resident in State C. State A and State C do not have a tax treaty in place. It can be observed that there is no BO in State B due to its obligation to pass the payment onto another party. Clearly, such payment is not made for the benefit of any resident in State B nor for enhancing economic cooperation between States A and B. Instead, the benefit would be received by the resident of a third State (i.e., State C). This clearly shows that the treaty has been misused or abused by the resident of State B, against the intention, object, and purpose of the treaty between States A and B.
To combat misuse of the treaty like the case described above, BEPS Action 6 seeks IF members to implement a ‘minimum standard’ in all its treaties. The minimum standard can be either of the following:
- The combined approach of a Limitation of Benefits (LOB) and a Principal Purpose Test (PPT) rule,
- The PPT rule alone, or
- The LOB rule supplemented by a mechanism that would deal with conduit financing arrangements not already dealt with in tax treaties.
As a consequence, many IF members’ tax treaties have been updated to include, at least, a PPT rule. This is done by way of signing and ratifying the Multilateral Instrument (MLI) as it allows IF members to update multiple bilateral tax treaties simultaneously. The PPT rule looks a lot like the MPT. True to its name, if one of the principal purposes of an arrangement is to obtain a benefit, the PPT rule may be triggered. This clear intention has also been expressed in the wordings of the preamble incorporated in the OECD Model Tax Convention 2017.
Due to the lack of case law, the impact of the PPT rule is rather uncertain for now and the interpretation of the PPT rule may vary across jurisdictions. It may be possible that the cases that were successfully tested before the courts of law earlier may not survive the PPT rule if they were to be presented before the courts today, provided that the PPT rule was applicable at the time of the transaction or arrangement.
What is certain is that taxpayers ought to be very careful in tax planning so that the structures do not fall foul of the PPT rule. When deciding on the country to make an investment in or the structure of a transaction or arrangement, taxpayers ought to clearly record the non-tax reasons (main/principal purposes) for selecting a certain jurisdiction over another. Evidence can be maintained through internal emails, memos, and minutes outlining the reasons for selecting a country. For example:
- A country is preferred due to a favourable corporate law regime.
- A country is preferred due to the presence of multilingual or highly qualified employees.
- A country is preferred as it is politically and socially stable.
- A country is preferred as it has a strong banking infrastructure where it is easy to obtain credit.
Despite the above safeguards, if the tax authority does reasonably conclude that one of the principal purposes of invoking the treaty was to obtain a tax benefit, the taxpayer ought to ensure that it can establish (i.e., prove) that the benefit obtained was indeed within the object and purpose of the tax treaty.
Finally, as mentioned before, public opinion against tax avoidance is stronger than ever. The relevance of the PPT to future transactions cannot be overstated. Arrangements that may have been successfully litigated before the courts of law until a few years ago, may not be as successful from now on. Therefore, taxpayers may find advance rulings to be attractive as it is important to avoid future issues.
It will be interesting to see how the UAE and the other GCC countries will approach such abusive arrangements and its possible disputes. In the meantime, it is apparent that either through the MLI or through bilateral double tax treaties, the PPT continues to be important. It is vital to consider such anti-avoidance provisions now in order to create future proof structures.
UAE Corporate Tax - Public Consultation Document
UAE Corporate Tax - Public Consultation Document
Download Aurifer’s reply to the Public Consultation initiated by the UAE Ministry of Finance in regard to the implementation of Corporate Income Tax in the UAE as of June 2023.
Scoring Tax Exemptions in Qatar
Scoring Tax Exemptions in Qatar
International sports bodies typically insist on obtaining widespread tax exemptions as a precondition to awarding the hosting rights to a bidder. This also applies for events organized by the Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA). FIFA’s biggest event, the Football World Cup, will kick off later this month in Qatar.
Obtaining tax exemptions is such a sensitive topic for sports organizations that there have even been instances where the events have entirely moved to another country because a country was unable to grant the exemption. For example, the T20 Cricket World Cup was moved from India to the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Oman last year because the Indian Government did not offer the exemptions in time.
In Qatar, even though Qatar has Free Zones, only the Qatar Financial Centre (QFC) issues its own tax framework. It applies next to the general tax framework applicable in the rest of the State of Qatar. We will be looking at these frameworks in this article.
Claiming Tax Exemptions (Substantive Aspects)
For mainland Qatar, Ministerial Decision No. 9 of 2022 (Ministerial Decision) issued earlier this year on 25 August 2022 = provides details on the exemptions available to different parties, based on Government Guarantee No. (3) dated 22 February 2010 (Government Guarantee) issued by the State of Qatar to FIFA.
The most comprehensive exemption benefits are provided to FIFA itself and its affiliates (whether residents or non-residents). They are totally exempt from any taxes.
Contractors are granted a limited exemption to the extent of all taxes on import, export or transfer of goods, services and rights related to the activities of the World Cup, if the goods are imported for their use by:
- The Contractors themselves in Qatar,
- The Contractors, with the possibility of re-exporting the goods,
- The Contractors, with the possibility to donate to sports entities, charitable foundations etc.
Individuals employed or appointed by the following, are also exempt from individual taxes on payments, fringe benefits or amounts paid or received in relation to the World Cup, until 31 December 2023:
- FIFA,
- FIFA’s affiliates,
- Continental or National Football Associations,
- Event broadcasters,
- Suppliers of goods,
- Works contractors and
- Service providers.
This exemption also covers Personal Income Taxes for those individuals who enter and exit Qatar between 60 days before the first match (21 September 2022) until 60 days after the final match (16 February 2023), as long as they do not permanently reside in Qatar. This exemption may be void of much effect, given the absence of Personal Income Tax in Qatar.
An Exemption from Excise tax is to be obtained by way of refund, by providing documents like purchase invoices and bank details.
Claiming The Exemptions - Logistical Aspects
For exemptions granted by the General Tax Authority (GTA), there is no requirement to register with the GTA. Instead, FIFA (through the Supreme Committee for Delivery and Legacy (Supreme Committee)) prepared a list of exempted entities and individual, containing data such as the nature of contracted works, term and value of the contract, and the residency of the contracting party.
The Supreme Committee then provides the GTA the relevant documentation (Articles of Associations of companies, addresses of individuals etc.) in regard to the organisation or individuals for whom the Tax Exemption is applied.
For claiming customs duty exemptions with the General Authority of Customs (GAC), (and unlike the procedure with the GTA), the claimants need to register with the GAC.
Here too, FIFA approves the list for the Supreme Committee to provide to the GAC to entitle those entities to exemptions from customs duties and fees. Based on this list, the GAC provides the listed entities amongst others with facilities in regard to electronic customs clearance.
In this regard, the GAC also earlier this year launched a ‘Sports Events Management System’ to facilitate customs procedures during sporting events, including the World Cup. This system provides electronic services for the clearance of goods, including easy registrations, accelerated customs procedures, and the inclusion of a special unit to facilitate approvals for incoming shipments.
There may be some interesting questions on the applicability of the Ministerial Decision, including:
- To what extent are the activities ‘directly or indirectly’ related to the activities of the World Cup? For example, does it include online betting platforms involved in placing bets on the matches? Would it include businesses that are involved in ancillary aspects to the World Cup such as general tourism consequent to the World Cup?
- Would match fee or advertisement / sponsorship / award income earned by the footballers in relation to the World Cup also be covered under the Ministerial Decision?
- Where an event broadcaster obtains substantial advertisement income from brand sponsors during the broadcast of the match or match related activities, is such income also exempt from taxes?
QFC - Tax Exemption Regime for the World Cup
The QFC in its Concessionary Statement of Practice (Statement) explicitly provides that a QFC entity which is a:
- FIFA subsidiary – is exempt from Corporation tax and any other charge, levy, penalty or interest related thereto;
- FIFA Host Broadcaster or a Local Organizing Committee (LoC) Entity – is exempt from Tax ‘in relation to taxable profits that are derived from activities carried on for the purposes of the World Cup’.
The major conditions for such QFC entities to claim the exemption are as follows:
- Such QFC entities have genuine economic substance in Qatar,
- The QFC entity operates in terms of the license and upon authorization of the Qatar Financial Centre Regulatory Authority (QFCRA),
- An Advanced Ruling has been applied for by the QFC entity and granted by the QFC, confirming the exempt status of such QFC entity,
- The QFC entity is included in the list provided by FIFA to the QFC Tax Department,
- The sole or main purpose of such QFC entity is not avoidance of tax,
- The QFC Tax Department is satisfied that granting the exemption is not in breach of international tax principles set out in the BEPS Project minimum standards.
The potential activities that can be developed in the QFC are limited, and therefore not all types of businesses can set up in the QFC.
No VAT – No VAT Exemption
Even though Qatar is a part of the GCC VAT Agreement and committed to implement VAT in the same vein as its neighboring countries of the UAE, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), Bahrain and Oman have done, it has not yet enacted any legislation.
Therefore, there is currently no need for a VAT exemption for the World Cup. Who knows, VAT may be introduced shortly after the organization of the World Cup?
Exemptions Worth the Trouble?
Granting tax exemptions for international sporting events are sometimes controversial. The public in some hosting countries do not always believe they receive a return on investments from the event. While Qatar has spent substantial amounts of money on the construction of infrastructure, the effect of the tax exemptions is rather limited, and at least for Qatar, it seems to have been worth the investment. In any case, the exemptions are a precondition, without which a country cannot bid. After the UAE had hosted the FIFA Club World Cup a number of times, Saudi Arabia will now be looking at hosting the Asian Winter Games in 2029. Those countries have given similar tax concessions to the international organizations managing the events.
For future possible events in the UAE, it will also be interesting to see how the sporting organizations and the tax authorities will deal with the Corporate Income Tax (CIT) which is to be introduced in the UAE in June 2023. The relationship may be anything between an unbridled and full-fledged exemption (if the UAE is willing to do so), or it may lead to rather interesting tax claims (like the Formula 1 case on Permanent Establishment (PE) in India a few years ago, which was decided by the courts in the tax authority’s favor). Time alone can tell.
Almost 5 years down the line for VAT in the GCC – what’s next?
Almost 5 years down the line for VAT in the GCC – what’s next?
Almost 5 years down the line for VAT in the GCC – what’s next?
As we approach 31 December 2022, the UAE and KSA will be celebrating 5 years of applying VAT. A rollercoaster ride for many in the region, authorities, advisers and in house tax managers.
We wrote in 2017 about the challenges of drafting VAT legislation in the GCC before its implementation (https://aurifer.tax/news/the-challenges-of-drafting-tax-legislation-and-implementing-a-vat-in-the-gcc/?lid=482&p=21).
We pondered whether the GCC was potentially going to be far ahead of other jurisdictions because of the Electronic Services System (“ESS”) the GCC VAT Agreement was going to implement, foreseen in article 71 of the Agreement (https://aurifer.tax/news/future-of-vat-in-the-eu/?lid=482&p=22). The GCC however never implemented the ESS. It is therefore missing an important instrument to integrate all GCC members under a single comprehensive regional VAT framework.
After almost 5 years, it’s worth taking a step back and looking at what occurred.
6 countries to implement, only 4 did
The GCC consists of six countries, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Bahrain, Oman, Kuwait and Qatar. All countries were supposed to introduce VAT in a short span of time. The UAE and KSA did so on 1 January 2018, Bahrain on 1 January 2019, and Oman on 16 April 2021. For Qatar, rumours ebb and flow on an implementation of VAT after the World Cup, but officials are tight lipped. In terms of Kuwait, a new government is not likely to put this on the table – at least, in the near future.
The intention to implement almost simultaneously was taken with the idea of avoiding arbitrage – considering the geographical proximity between the states - and potential issues with fraud.
5% was supposed to be the rate
All 4 countries kicked off with 5% VAT, as it is foreseen in the GCC VAT Agreement as well (article 25). Saudi Arabia was the first one to hike the rate to 15% on 1 July 2020. Bahrain increased to 10% on 1 January 2022.
The increases were implemented for the same reason, as the tax was implemented for in the first place, i.e. fiscal stability. The implementation came off the back of a protracted period of running deficits for many Gulf countries. There is currently a bounce back, but how long it will take is unclear, and therefore hard to predict whether it will impact fiscal policy in the short run.
Saudi Arabia, by way of its Finance Minister, had already stated in 2021 that it would consider revising the VAT rate downwards after the pandemic. If it will happen, it will happen soon.
It’s safe to say the other GCC countries could still revise the rate upwards or downwards, depending on their specific fiscal situation.
Interestingly, the increase of the VAT rate to 15% also spawned a new tax in KSA, the Real Estate Transfer Tax (“RETT”). This new tax in KSA aimed to solve the issue of unregistered sellers, and reduce the taxes on real estate sales. Since its introduction, the RETT legislation has been amended multiple times.
The GCC countries were supposed to have numerical VAT numbers, Oman didn’t follow
In the framework of the GCC, the idea was floated to have numbers as VAT numbers. Hence, the UAE has a 1 before the number, Bahrain a 2 and Saudi a 3. Oman however choose letters and put “OM” before the number.
In the EU, VAT numbers are also composed of letters and numbers. Two letters make up the first two symbols of the VAT number and refer to a country, e.g. “LU” refers to Luxembourg (see https://taxation-customs.ec.europa.eu/vat-identification-numbers_en).
Zero rates for services are perceived a complication
5 years in, the application to zero-rate VAT on exported services, i.e., services provided to recipients outside of the GCC, remains complicated for businesses to apply and inconsistent between the GCC member states.
Although the GCC VAT Agreement for place of supply purposes looks like the EU VAT directive, from the outset, each GCC member state chose different approaches towards the place of supply of services.
B2B services were not simply located in the country of the recipient, as they are in the EU since 2010, and as is recommended by the OECD in its VAT/GST Guidelines on B2B services.
Based on an interpretation of article 34(1)(c) of the GCC VAT Agreement as laying down the rule, and including a benefit test, GCC countries have embarked on a conservative and selective interpretation of the zero rate on supplies made from a GCC country to abroad.
That conservative interpretation is not necessarily mirrored when those services are received, as there is no benefit test required there.
The rule is therefore applied unequal, and as shown by both the UAE and KSA, they felt the rule required amendments to the provision itself (https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/uae-considerably-restricts-application-vat-zero-rate-services-vanhee/). Those amendments, and ensuing clarifications have not necessarily led to more clarity.
Unfortunately, Bahrain and Oman went down the same road. A too conservative view of zero rates, can put a strain on foreign investments, as it is not easy to obtain refunds for foreign businesses (as amongst others the Saudi example shows).
As a matter of fact, disputes are common among businesses in the GCC over the VAT treatment of cross-border services due to the difference in the domestic legislation between the GCC member states and in the absence of the ESS.
Divergent policy options
The GCC VAT Framework Agreement allowed for broad policy options in the education sector, health sector, real estate sector and local transport sector. In addition, for the oil & gas sector zero rates were allowed to be implemented as well, and the financial sector could benefit from a deviating regime as well. Depending on the individual requirements and policies, the GCC Member States have implemented substantially different regimes.
None of the GCC countries so far have amended those policies in the aforementioned sectors. The UAE did move from a system where the B2B sales of diamonds was taxed, to a system where it is subject to a reverse charge as from 1 June 2018.
Tax Authority approaches
So far, in the region ZATCA has shown the most grit in terms of audits, and has lengths ahead of the other countries in terms of tax audits and disputes. KSA also had the best equipped tax authority in 2018 when VAT was introduced, although it did have to go through an organizational revamp. The UAE comes second, which is remarkable for a tax authority which only kicked off in 2017. It has been very much a rules and process based organization, which has a lot of positive effects, such as tax payers feeling treated in the same way. UAE auditors now often also give the opportunity to tax payers to voluntarily disclose their liabilities before closing the audit, which is a novely approach in the region.
The Bahraini and Omani tax authority, have been taking a more relaxed approach towards audits and disputes.
Having said the above, it's all not all 'sticks' with the tax authorities. We have also observed in this 5 years, how the tax authorities, especially in KSA and the UAE, played a their role to alleviate tax from being a burden to businesses and encouraging tax compliance - a fairly new culture of this scale. The amnesty programmes, first introduced by the KSA in 2020 and again, recently paved the way on encouraging tax compliance for businesses. The UAE also introduced their amnesty programme this year with the same intention. Perhaps, this could be a temporary solution to gear the economy back on track post pandemic. On whether it will be the norm, is yet to be seen in the next coming years.
What the future will bring
An old-fashioned system was put in place, yet one that has proven its use in revenue collection. It also worked, given the substantial revenues gained from VAT.
The GCC did not opted to immediately adopt more modern, electronic systems as these exist elsewhere (e.g. since a long time in Brazil, but also China).
However, it was identified that E-invoicing was the way to go in the medium run. This is again trodding down a proven path. As often in the GCC, the UAE and KSA show the way. KSA has made E-invoicing mandatory. The UAE and Bahrain have already suggested they will do the same very soon.
No GCC countries have yet announced they will adopt real-time reporting. KSA may be the closest to a potential adoption, given that once phase 2 enters into force in 2023, ZATCA, the KSA tax authority will have access to substantial transactional data. It will allow it to pre-fill the VAT return, and potentially even in real time calculate the VAT.
We'll see what the future will bring, and for sure in another five years matters will have evolved again drastically, given the pace of changes in the region.
Safe to say that the next 5 years will be equally exciting.
How anti-avoidance provisions can curtail the application of Double Tax Treaties, including in the UAE?
The Ministry of Finance (MoF) of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) recently announced that the draft Corporate Tax (CT) law is going to be released soon, and likely within the month of September. This is impactful news for businesses in the UAE. Many businesses are already in the process of taking steps to plan their affairs in such a way that their operations are tax compliant and tax optimized at the same time.
The UAE’s international position will change after the implementation of corporate tax. Some jurisdictions may no longer view the UAE as a tax haven (although the Free Zone businesses may still benefit from a 0% rate). Other tax authorities may therefore change their perspective on the UAE and be more inclined to grant the benefits under the double tax treaties.
Businesses on the other hand, will no longer view the UAE as a conduit jurisdiction with an extensive treaty network, through which they can avail tax treaty benefits. While the 9% headline rate is still comparatively low, the implementation of CT may also discourage taxpayers seeking out the UAE solely for tax purposes.
A recurring point of dispute between the tax authority and businesses in almost every country having a CT regime has been drawing the line between tax planning, tax avoidance and tax evasion. Once the UAE CT regime settles, the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) of the UAE may indeed pay more attention towards countering tax avoidance and tax evasion arrangements or transactions.
In this article, we will revisit the evergreen discussion of tax planning, tax avoidance and tax evasion, with an emphasis on the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). To begin, let us examine the meaning of the terms tax avoidance and tax evasion and the differences between the two terms.
Tax avoidance has traditionally been considered as lawful. It can be described as planning for the purposes of minimizing the tax burden within the legal framework. Tax evasion on the other hand is considered unlawful, and often requires an intentional and a potential fraudulent element.
In the GCC, tax authorities resort rather quickly to suggesting a taxpayer has committed tax evasion, even when the situation concerns simple non-compliance.
While not considered unlawful, tax avoidance has been considered harmful. This is why countries around the world, including the GCC Member States, are implementing domestic rules to counter aggressive or harmful tax planning in line with international standards.
The OECD tried to address this point by way of the ‘Main Purpose Test’ (MPT). The MPT was included in the OECD’s Model Tax Convention in its 2003 version. We are paraphrasing, but the principle stated that benefits under a double tax treaty should not be granted where the main purpose of setting up a structure was for tax purposes as the tax benefits resulting from that structure would go counter the object and purpose of those treaties.
Another common mechanism proposed in tax treaties to avoid the improper use of tax treaties, is the ‘Beneficial Ownership’ (BO) requirement. It mainly applies to passive income (e.g., dividends, interests, and royalties). The BO concept provides that where an item of income is paid to a resident of a Contracting State acting in the capacity of an agent or a nominee, it would be inconsistent with the object and purpose of the source state to grant an exemption or relief, merely because the direct recipient is a resident of the other Contracting State. In such a case, the direct recipient, on account of being merely an agent, nominee, conduit, fiduciary, or administrator, would not be able to obtain the benefits of the treaty. This is especially evident if such recipient is legally or contractually bound to pass on the payment received to another person. BO disputes often end up before the courts, because the burden of proof for the taxpayer is not easily met.
The 2008 Financial Crisis put the discussion on tax avoidance and aggressive tax planning firmly on governments’ agenda. Following the Financial Crisis, public opinion shifted towards ensuring that big corporations pay their fair share of taxes and pressured countries to implement rules to discourage such behaviors.
As a result, the OECD established what is known as the ‘Inclusive Framework’ (IF), which was open to both OECD and non-OECD members (currently at 141 members) to engage in discussions and create rules for countering Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS). It is formally known as the OECD/G20 BEPS Project (BEPS Project 1.0) which identified 15 Action Points in 2015.
Out of the 15 Action Points, one of the most important action plans was BEPS Action 6 - Prevention of Tax Treaty Abuse, which also formed one of the four minimum standards. BEPS Action 6 addresses treaty shopping activities that would be viewed as avoidance.
BEPS Action 6 requires IF members, amongst others, to include an express statement in their treaties that their common intention is to eliminate double taxation without creating opportunities for non-taxation or reduced taxation through tax evasion or avoidance, including through treaty shopping arrangements.
Anti-avoidance rules aim amongst others to avoid conduit arrangements. For example, State A has a domestic withholding tax rate for dividends of 25%. State A and State B have negotiated a tax treaty where the source withholding tax rate for dividends is reduced to 5%. A resident in State B receives dividends from State A and claims the reduced treaty rate of 5% source withholding.
However, the resident in State B has an obligation to redistribute the dividend income to a resident in State C. State A and State C do not have a tax treaty in place. It can be observed that there is no BO in State B due to its obligation to pass the payment onto another party. Clearly, such payment is not made for the benefit of any resident in State B nor for enhancing economic cooperation between States A and B. Instead, the benefit would be received by the resident of a third State (i.e., State C). This clearly shows that the treaty has been misused or abused by the resident of State B, against the intention, object, and purpose of the treaty between States A and B.
To combat misuse of the treaty like the case described above, BEPS Action 6 seeks IF members to implement a ‘minimum standard’ in all its treaties. The minimum standard can be either of the following:
- The combined approach of a Limitation of Benefits (LOB) and a Principal Purpose Test (PPT) rule,
- The PPT rule alone, or
- The LOB rule supplemented by a mechanism that would deal with conduit financing arrangements not already dealt with in tax treaties.
As a consequence, many IF members’ tax treaties have been updated to include, at least, a PPT rule. This is done by way of signing and ratifying the Multilateral Instrument (MLI) as it allows IF members to update multiple bilateral tax treaties simultaneously. The PPT rule looks a lot like the MPT. True to its name, if one of the principal purposes of an arrangement is to obtain a benefit, the PPT rule may be triggered. This clear intention has also been expressed in the wordings of the preamble incorporated in the OECD Model Tax Convention 2017.
Due to the lack of case law, the impact of the PPT rule is rather uncertain for now and the interpretation of the PPT rule may vary across jurisdictions. It may be possible that the cases that were successfully tested before the courts of law earlier may not survive the PPT rule if they were to be presented before the courts today, provided that the PPT rule was applicable at the time of the transaction or arrangement.
What is certain is that taxpayers ought to be very careful in tax planning so that the structures do not fall foul of the PPT rule. When deciding on the country to make an investment in or the structure of a transaction or arrangement, taxpayers ought to clearly record the non-tax reasons (main/principal purposes) for selecting a certain jurisdiction over another. Evidence can be maintained through internal emails, memos, and minutes outlining the reasons for selecting a country. For example:
- A country is preferred due to a favourable corporate law regime.
- A country is preferred due to the presence of multilingual or highly qualified employees.
- A country is preferred as it is politically and socially stable.
- A country is preferred as it has a strong banking infrastructure where it is easy to obtain credit.
Despite the above safeguards, if the tax authority does reasonably conclude that one of the principal purposes of invoking the treaty was to obtain a tax benefit, the taxpayer ought to ensure that it can establish (i.e., prove) that the benefit obtained was indeed within the object and purpose of the tax treaty.
Finally, as mentioned before, public opinion against tax avoidance is stronger than ever. The relevance of the PPT to future transactions cannot be overstated. Arrangements that may have been successfully litigated before the courts of law until a few years ago, may not be as successful from now on. Therefore, taxpayers may find advance rulings to be attractive as it is important to avoid future issues.
It will be interesting to see how the UAE and the other GCC countries will approach such abusive arrangements and its possible disputes. In the meantime, it is apparent that either through the MLI or through bilateral double tax treaties, the PPT continues to be important. It is vital to consider such anti-avoidance provisions now in order to create future proof structures.
UAE VAT for foreign businesses
With the influx of more than 25 million visitors expected from around 190 countries for Expo 2020, the UAE FTA has implemented two special VAT refund mechanisms to ensure that business visitors do not incur any VAT.
The first mechanism targets exhibitions and conferences attended by international businesses. The second one benefits business visitors who will be able to claim the refund of VAT paid on expenses incurred in UAE. Below the two mechanisms are discussed.
VAT refund for exhibitions and conferences
The VAT refund for exhibitions and conferences is beneficial for the organizers as well as the business visitors attending such events in the UAE.
This scheme enables both suppliers and their international customers to save 5% VAT payment on selected services. This particular refund mechanism covers services such as the rental of exhibition space or access to exhibitions and conferences.
Only international customers, those who are not established in the UAE or are not registered for VAT purposes in the country, can avail this benefit. The international customer must inform the supplier that the business is not resident in any manner or registered in the UAE for VAT purposes.
The supplier, on the other hand, needs to be registered for VAT purposes in the UAE, as well as inform the FTA before the event takes place to be able to grant this benefit to its international customers.
Once registered, the conference and exhibition supplier should issue an invoice with VAT but not collect VAT on the relevant exhibition or conference services from their customers. Instead, he claims the VAT refund equal to the output VAT charged on the subsequent VAT return.
Since the payment of this VAT will de be deferred to the VAT return and compensated with a simultaneous deduction in the same return, it does not impact the supplier’s cash flow, while also providing the customers with immediate VAT refund.
Refund for business visitors
Similar to the business VAT refund scheme available in the European Union, the UAE has implemented a scheme whereby all VAT costs incurred by a non-resident business which are not registered for VAT in the UAE, are reimbursable through the VAT refund mechanism for business visitors.
Some of the most common expenses by non-residents include the local purchase of goods, employee travel and lodging, training, service charges for vendors and others. It is important to note that the VAT reclaimed must be directly related to the business activities and cannot be for entertainment or any other legally blocked expense, which are specifically excluded from all input VAT recovery.
Foreign business will only be entitled to claim a VAT refund in case they are from a country that has VAT and also provides refunds of VAT to UAE entities in similar circumstances. KSA currently does not provide this refund to UAE businesses. Therefore, the UAE will also not refund businesses from KSA.
The minimum amount of each application for refund of tax is AED 2,000 which may be the amount of single or multiple purchases. The application should be submitted by a calendar year. The FTA will start receiving claims in respect of VAT incurred in 2018 as from April 2019. The opening date for refund applications in subsequent calendar years will be 1st March.
The FTA will soon release further guidance concerning the exact process for claiming the VAT refund. However, it is expected that businesses will have to provide the original tax invoices for which they intend to reclaim the VAT as part of the application.
VAT obligations for non-resident business
Conferences and exhibitions generate significant opportunities for businesses to show their products and close some deals.
However, non-resident businesses who intend to sell goods or provide services during a conference or exhibition in the UAE might need to assess their VAT obligations in the country. For non established businesses, the obligation to register for VAT purposes with the FTA arises from the first taxable supply.
Importantly, non-resident businesses making taxable supplies in the UAE are not entitled to the business visitor refund scheme or to benefit from the VAT refund for exhibitions and conferences.
Overall, these guidelines will not only put UAE top of the list for the hosting of conferences and exhibitions, but it also encourages conference and exhibitions providers, as well as international customers to organize and attend such events in the UAE.
KSA releases draft Transfer Pricing regulations for consultation
KSA releases draft Transfer Pricing regulations for consultation
Early 2010’s, following the financial crisis and multiple tax scandals, such as the Panama papers and LuxLeaks, the BEPS initiative was launched by the OECD and the G20. The BEPS initiative is a set of international recommendations meant to prevent Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (international tax avoidance).
As part of the BEPS initiative, Transfer Pricing (TP) rules were put on the agenda worldwide as a means to avoid tax evasion. The first detailed and comprehensive TP rules were designed in the 1990’s. The US published regulations in 1994 and the OECD published guidelines in 1995.
Saudi Arabia is member of the G20 and was expected to adopt a comprehensive set of rules to tackle tax avoidance through transfer pricing rules. Recently, it published draft By-Laws on Transfer Pricing. This draft remains available for public comments till 9 January 2019.
KSA’s Income Tax Law had already implemented general anti-TP avoidance measures and approved the arm’s length principle, similar to other GCC Member States. However, these new By-Laws are going a lot further in terms of defining the applicable transfer pricing principles and documentary requirements. The new obligations trigger important compliance obligations and require extensive preparation.
What is a transfer price?
A transfer price is the price agreed between entities of a same group for their internal transactions (‘controlled transactions’). It targets the relocation of profit within the Group: one entity located in a tax haven invoices its supplies (services or goods) at an artificially high price to another entity located in a high tax jurisdiction, successfully decreasing its taxable base.
In order to avoid this artificial profit shifting, the transfer price is required to comply with the arm’s length principle. This principle requests that the controlled transaction price is determined as if the transactions were made between unrelated parties.
What’s new?
The draft determines the applicable methods and documentation inspired directly by the OECD guidelines and BEPS reports.
Transfer Pricing Methods
KSA has approved the 5 OECD transfer pricing methods:
- Comparable Uncontrolled Price Method
- Resale Price Method
- Cost Plus Method
- Transactional Net Margin Method
- Transactional Profit Split Method
A transfer pricing method other than the ones above can be adopted, provided the taxable person can prove that none of those methods provides a reliable measure of an arm’s-length result.
Documentation
In line with the OECD recommendations, KSA requires:- A Master File and Local File to detail the Group and entities' transfer pricing policy (notably an explanation of the applied transfer pricing method) to be prepared on an annual basis at the time of the income tax declaration (only for MNE Group with an aggregate arm’s length value of controlled transactions exceeding SAR 6,000,000 during any 12 month period);
- The Country by Country Report (CbCR) to be submitted no later than 12 months after the end of the concerned reporting year for MNE groups with a consolidated turnover of more than SAR 3.2 billion.
In addition, it requires a 'Controlled Transaction Disclosure Form’ to be submitted on an annual basis along with the income tax declaration (no threshold applies).
The draft By-Laws draft do not mention the language in which the documentation is to be maintained and filed. However, since the documents are to be submitted together with the income tax declaration, it is likely that TP documentation will have to be in Arabic as well.
It is important to note that these obligations are already applicable to fiscal years ending on 31 December 2018. This implies that the concerned companies must start preparing the required documentation. The latter must be ready within 120 days following the end of the fiscal year, i.e. by the end of April 2019 for the first concerned MNEs.
Exceptions
The draft contains certain exceptions for maintaining the Local file and the Master file. Are exempted from these obligations:
- Natural persons;
- Small Size Enterprises;
- Legal persons who do not enter into Controlled Transactions, or who are a party to Controlled Transactions where the aggregate arm’s-length value does not exceed SAR 6,000,000 during any 12 month period.
Adjustments
Where the price is not at arm’s length, GAZT can adjust the tax base accordingly. This can result in a higher tax liability if part of a tax deduction is rejected or if it considered that the KSA entity should have charged a higher price to its foreign affiliate.
GAZT can also be informed of any TP adjustments made in another country, on a controlled transaction made with a KSA resident, if a treaty is in place with this country. GAZT can ensure the changes by the foreign authority are in line with the arm’s length principle. GAZT can subsequently make the appropriate adjustment to take into account the increase in the taxable base by the foreign tax authority.
In case GAZT disagrees with the adjustment, it can communicate and discuss with the respective foreign authority. An existing mutual agreement procedure ('MAP') with the foreign authority will be necessary.
Advance Pricing Agreements
An APA can safeguard companies against tax reassessments, as it provides for an agreed transfer price by the Tax Authority regarding specific transactions.
The draft By-Laws do not currently provide for an Advance Pricing Agreements (APA) procedure. We may expect some guidelines from GAZT concerning this matter.
Tax Audit and penalties
GAZT has been working on TP for many years and is well prepared to enforce the new TP requirements. A specific tax unit, with experienced auditors, has been created to guarantee the correct implementation of these laws.
The draft By-Laws do not foresee penalties in case of non-compliance. However, it is highly likely that the common penalties relating to corporate income tax would apply. We expect more guidelines soon.
Impact on the GCC
Any GCC company performing controlled transactions with a KSA company will have to comply with the KSA TP rules. The valuation of its intra-group sales must comply with the valuation methods recommended by the KSA TP rules.
In addition, GCC affiliates with a KSA headquarter will have to prepare a local file describing their own transfer pricing policy for the transactions with their KSA related parties. Important accounting information will also have to be gathered and transmitted to the KSA headquarter to be compiled in the CbCR.
Concerned entities must start to plan immediately. Practically this does not only encompass preparing the documentation. Companies must also keep evidence of the invoiced work, especially when intangible (e.g. management fees might be requested to be evidenced by proof of rendered services: announcements of internal seminars, memoranda, presentations, emails…). This implies to retain all data regarding intra-group transactions and to draft and maintain the required documentation or information and keep it up to date.
Finally, these new KSA By-Laws open the door to the implementation of TP rules in the other GCC countries, and notably in the UAE. The UAE committed to introducing a CbCR by joining the BEPS Inclusive Framework earlier this year.
Bahrain releases further information on VAT
- 20 December 2018: businesses with turnover > BD 5 million, effective date is 1 January 2019.
- 20 June 2019: businesses with turnover > BD 500,000, effective date is 1 July 2019.
- 20 December 2019: businesses with turnover > BD 37,500, effective date is 1 January 2020.
- Quarterly in 2019: businesses with turnover > BD 5 million.
- Semi-annual in 2019: businesses with turnover < BD 5 million.
- Monthly in 2020: businesses with turnover > BD 3 million.
- Quarterly in 2020: businesses with turnover < BD 3 million.
- No requirement for invoices to be in Arabic.
- Simplified invoices can be issued for supplies to non-registered customers and for supplies with an amount < BD 500.
- Bank statements will be valid as tax invoices for banks.
- The required mentions on the invoices will be similar to KSA’s rules and the potential number of the required mentions will be around 14.
- Zero rate: construction of all buildings (residential and commercial).
- Exempt: sale and lease of all buildings (residential and commercial) and bare land.
- Dividends are out of scope of VAT.
- Life insurances are exempt from VAT, all other insurances are subject to VAT.
The impact of the US tax reform on the GCC
The impact of the US tax reform on the GCC
It represents a major change to the US tax system, holding high significance particularly to multinational companies and the US economy as a whole.
In the long term, the reform is predicted to raise the US GDP and wages, assuming that the tax cuts will provide increased stimulus for investment and activities, thereby increasing labor demand. These new incentives and deterrents have consequences on the foreign investments of US companies, including in the GCC region.
WHAT’S HAPPENED?
The US Tax Cuts and Jobs Act entered into force on 1 January 2018 is meant to significantly positively impact businesses.
Through this reform, along with an important reduction of the corporate income tax rate, another major change in the US taxation system appeared: the worldwide US taxation system has been switched to one that is very close in nature to a territorial system. This shift is accompanied by a “transition tax” and implies that corporations doing business abroad will no longer be taxed by the US on the profits they generate overseas.
While the reform brings restrictions on interest and loss deductions, related party payments and movements of intangible property (IP), it also introduces favorable dividend exemptions, capital investmentand exportincentives. This will ideally provide the necessary push to repatriate reserves of cash held overseas.
The reform also introduces new anti-avoidance and incentive tax measures, namely the Base Erosion and Anti-Abuse Tax (BEAT), the Global Intangible Low Taxed Income (GILTI) and the Foreign Direct Intangible Income (FDII).
IMPACT ON US BUSINESSES
1. Corporate Income Tax Rate Reduction
The main feature of the US tax reform is definitely the reduction of the Federal Corporate Income Tax (CIT) from 35% to 21%, starting from tax years beginning after 1 January 2018, with an average drop from 39% to 26%, including state income taxes.
This 26% CIT rate will be in line with the average among Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) member nations.
2. Interest Expense Deduction Limitation
This new provision provides for a limitation of the interest deduction for all business interest expenses paid by the taxpayer, namely interest paid or accrued on debt which can be traced back to a trade or business.
This new restriction applies to all businesses, regardless of entity type, at the legal entity level. This includes “C corporations” which are taxed separately from their owners and subject to corporate income taxation, and “S corporations” which' shareholders are directly subject to tax on their pro-rata shares of income based on their shareholdings (e.g. sole proprietorship).
However, this restriction does not affect small businesses since it applies only if the taxpayer’s average annual gross receipts for the three tax year period ending with the prior tax period do not exceed $25 million. Certain regulated public utilities, real estate and farming businesses that use the alternative (generally straight line) depreciation system for particular properties are allowed to elect for an exemption of this limitation.
This new measure, subject to some exceptions, limits the deductibility of interest to 30% of the “adjusted taxable income”. This “adjusted taxable income” can be largely compared to earnings before interest, depreciation, depletion, interest income, interest expense and amortization (EBITDA) for the first four years till 2022. From 2022 onwards, the limitation will be applied on an amount closer to the EBIT of the company. Any disallowed business interest deduction can be carried forward indefinitely.
This restriction on interest expense deduction was designed to deter companies from shifting debt financing to foreign subsidiaries, thereby discouraging cross company loans and borrowing for tax avoidance.
3. Loss restriction
The treatment of the Net Operating Losses (NOLs), the carry back and carry forward provisions were notably modified by the reform. The NOLs deduction is now limited to 80% of the taxable income of the year.
Previously, the NOLs offset was not limited and could be carried forward up to 20 years and carried back up to two years for corporate income tax purposes. With the reform, the carry back is eliminated while the carry forward is allowed indefinitely.
The reform only applies to NOLs generated in taxable years ending after 31 December 2017. Subject to limitations, NOLs generated earlier will be subject to the former rules. Therefore, taxpayers have to track NOLs depending on the year of their generation.
This reform aims at dissuading companies from bringing losses to the US to artificially reduce their profit and shift costs including interest to foreign affiliates to make better use of loss deductions.
4. Foreign Participation Exemption:
US parent companies who own at least 10% of a foreign group or affiliates are exempt from tax on dividends received from these companies. The ownership criterion can alternatively be the number of voting shares or their value.
The objective is to encourage US multinationals to shift their foreign profits onshore, since they can now bring cash back without heavy tax liabilities.
This exemption will not apply to any “hybrid dividend”, defined as any dividend for which the foreign affiliate received a deduction for local income tax purposes. This might notably happen when the capital provided to the foreign affiliate is deemed as a loan and grants the right to interest deduction to the foreign company, while the return on the same capital would classify as dividends in the US and be exempt. This would result in a double tax deduction on these amounts.
5. Transition Tax:
The inclusion of a transition tax is a strong signal that the US tax reform will confer many benefits from the territorial tax system but comes with compensation.
Current overseas untaxed earnings still accumulated and held abroad since 1986 will be subject to a one-time transitional tax payable over 8 years. This applies to controlled foreign corporations (CFC) or any other foreign companies with a 10% US corporate shareholder. The law refers to them as “Specified Foreign Corporations” (SFC).
The untaxed earnings would be charged at a lower rate of 15.5% for earnings held in cash or specified asset. Such items include:
- net accounts receivable,
- actively traded personal property, and
- obligations with a term of less than a year.
Any remainder will be taxable at 8%.
US shareholders are allowed to opt to pay the transition tax over eight years:
- 8% each year during the first five years,
- 15% the 6th year,
- 20% the 7th year,
- 25% the 8th year.
In case the US corporation does not pay this tax within 10 years of the Act’s enactment, a safety net ensures that the full amount of untaxed earnings is subject to the transitional tax to a 35% tax rate.
This is directed at increasing the amount of corporate cash available for M&A transactions and overall increasing the liquidity levels in the US.
This computation may present extreme complexity as there is a need to determine post-1986 earning pools and historic tax payments to substantiate any foreign tax credit attributable to post-1986 earnings. This would potentially require companies to arrange significant cashflow needed to pay tax.
6. Capital investment:
The previous bonus depreciation percentage which qualified property could benefit from has been increased, following the reform, from 50% to 100%, from September 2017 up to the end of 2022.
Accordingly, a company that acquires assets may be able to immediately deduct a significant portion of the purchase price as compared to the acquisition of the equity interests.
Beginning 2023, this bonus depreciation will be phased-out till 2026 (i.e. 80% for qualified property placed in service before 1 January 2024, 60% before 1 January 2025; 40% before 1 January 2026; and 20% before 1 January 2027).
The bonus depreciation is also applicable to non-original first use property as long as it is the tax payer’s first use.
This provision encourages structuring investments in new ways to take advantage of the deductions in the US along with the reduced effective tax rate as compared to other regions like Europe, Asia and Latin America.
7. Base erosion and anti-avoidance tax (BEAT):
The BEAT is introduced amid a global crackdown against companies which have used the world’s tax regimes and deprived governments of a large chunk of corporate revenue, estimated at USD 100-240 billion.
According to the BEAT, if a large multinational, operating in the US makes related-party payments that are potentially part of aggressive profit shifting, they will be subject to a new minimum tax.
BEAT only applies to companies:
- with average annual gross receipts of at least $500 million for the most-recent three year period, and
- with related-party deductible payments of 3% (2% for banks) or more of their total deductions for the year (the “base erosion percentage”).
These related party disallowed payments include royalties, interest, rent, high-margin service payments to a foreign related party for the purposes of avoiding tax but exclude most cost of goods sold, payment for services at cost and certain qualified derivative payments.
Computation is done by using a minimum rate of tax a company should be paying on income without disallowed payments (Modified Taxable income or MTI), comparing this to the regular tax liability of the taxpayer arising at the federal corporate tax rate. If the regular tax liability is lower than the minimum computation, the excess is the BEAT amount to be paid as an additional tax.
The minimum rate of tax to be used for this calculation is 5% of the MTI for year one, 10% thereafter and increasing to 12.5% from 2025 (additional 1% for banks and broker-dealers).
The BEAT is of major concern to foreign subsidiaries and could lead to a significant increase in US tax liability. Companies may find it beneficial to establish contracts in such manner that cost-sharing contracts between parents and subsidiaries are used instead of transactional payments in order to avoid the profit shifting arrangement.
8. Global intangible low tax income (GILTI):
This regime taxes the intangible low taxed income received from CFCs in the hands of the US shareholders.
This tax is charged on an accrual system where the US parent includes in their income the GILTI value to be fully taxed regardless of whether it is remitted back to the US or not. This decreases the benefit for US companies to shift their IP in foreign low tax jurisdictions.
The GILTI amount is calculated on a net deemed tangible return based on the CFC’s tangible assets, which equal 10% of the shareholder’s aggregate pro rata share of the CFC’s qualified business asset investment (QBAI). The QBAI can be defined as the CFC’s quarterly average tax basis in depreciable tangible property used in the CFC’s trade or business to produce tested income or loss.
The GILTI requires also to determine the US shareholder’s aggregate pro rata shares of its CFCs’ “net tested income”, which corresponds to the difference between the “tested income” (Gross income of a CFC excluding several listed incomes) and the specific “tested losses”.
The portion of the CFC’s net tested income that exceeds the deemed tangible return on tangible assets is then included in the U.S. shareholder’s GILTI amount.
For C corporations only, a deemed deduction of 50% will be applied to the GILTI amount but subject to a taxable income limitation. 80% of certain foreign income taxes paid by the CFCs will be deductible from the GILTI tax amount.
If the foreign effective tax rate on GILTI is at least 13.125% the US residual tax on the GILTI can be eliminated. If no foreign tax applies on the GILTI, US will tax this amount at a default rate of 10.5%.
9. Deduction for foreign derived intangible income (FDII):
While the tax reform uses GILTI to penalize taxpayers that have migrated IP offshore, it simultaneously incentives companies that leave their valuable IP in the U.S. using the FDII.
This provision grants a preferential effective tax rate of 13.125% to eligible income of C companies. This is relevant to US headquartered companies and non-US companies doing business in the US.
FDII can be defined as the net domestic income earned thanks to operations in the US but only related to export (sales, services, lease…).
Similarly to GILTI, the FDII is the part of the income of the US company that exceeds the deemed tangible return amount calculated with reference to the QBAI.
IMPACT ON BUSINESSES IN THE GCC
In the aftermath of the US reform, companies around the world will look to alter their policies to maintain their corporate revenue and tax advantages.
Some GCC countries have almost no corporate tax (i.e. UAE, Bahrain) and are, similar to other jurisdictions, being affected by the aforementioned measures. It would prove beneficial for US subsidiaries in the GCC to assess the extent to which costs have been shifted to them from the US. It is also expected that lower budgets will now be allocated to these subsidiaries, to hold cash within the US, impacting the available cash in the GCC.
Adversely, GCC headquarters with US affiliates will be impacted by the BEAT, as a transfer pricing inter-company loan component. Any major cash remittances back to the GCC parent will be under scrutiny for anti-tax avoidance purposes.